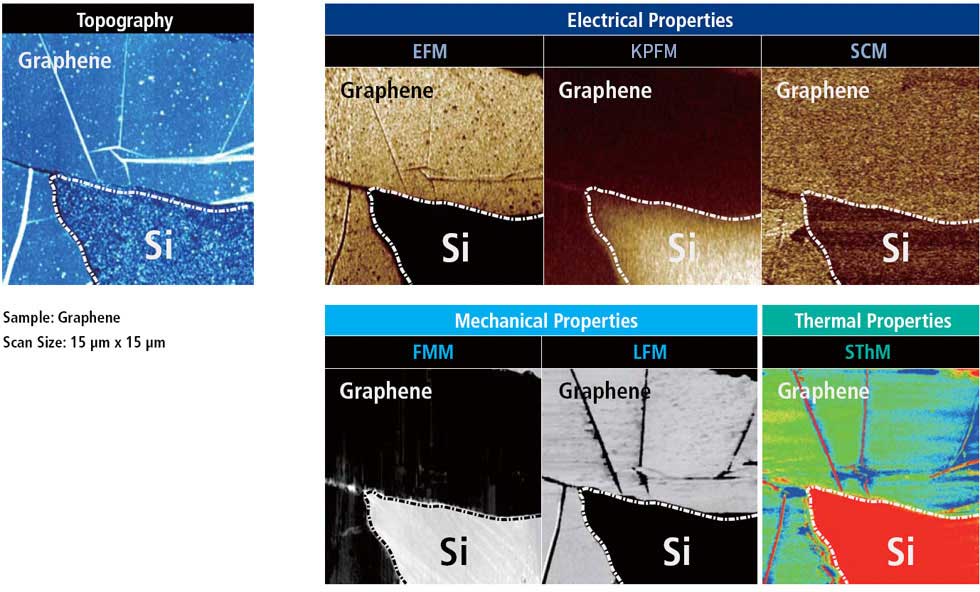
Description
Park XE15 MultiSample™ scan system
- Automated imaging of multiple samples in one pass
- Specially designed multi-sample chuck for the loading of up to 16 individual samples
- Fully motorized XY sample stage travels up to 150 mm x 150 mm
Using the motorized sample stage, MultiSample Scan™ enables programmable multiple region imaging in step-and-scan automation.
Here’s how it works:
1. Register multiple scan positions defined by a user
2. Image from the first scan position
3. Lift a cantilever
4. Move the motorized stage to the next user-defined coordinate
5. Approach
6. Repeat scan
The registration of multiple scan positions are easily carried out by either entering sample-stage coordinates or sample de-skewing by two reference points. This automated feature greatly increases productivity by reducing the need for your interaction during the scan process.
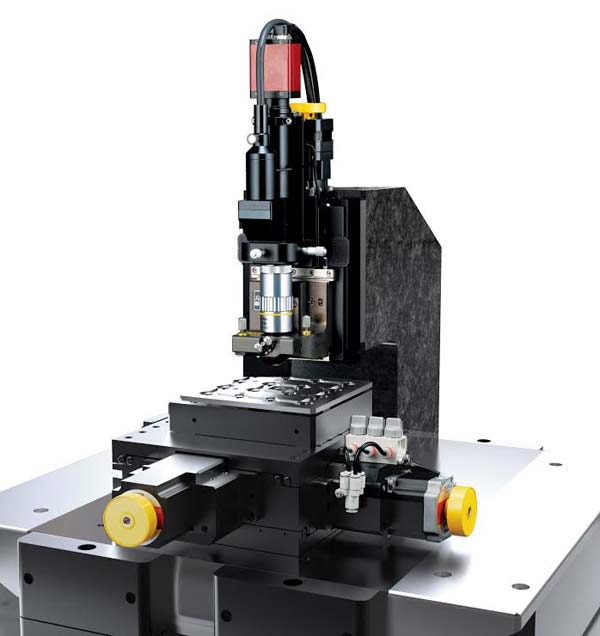

Accurate XY Scan by Crosstalk Elimination
Park Systems’ advanced Crosstalk Elimination (XE) scan system effectively addresses all of the above-mentioned problems. In this configuration, we used a 2-dimensional flexure stage to scan the sample in only the XY direction, and a stacked piezoelectric actuator to scan the probe cantilever in the Z direction only. The flexure stage used for the XY scanner is made of solid aluminum. It demonstrates high orthogonality and an excellent out-of-plane motion profile. The flexure stage can scan large samples (~1 kg) up to a few 100 Hz in the XY direction. This scan speed is sufficient because the bandwidth requirement for the XY axes is much lower than that for the Z axis. The stacked piezoelectric actuator for the Z-scanner has a high resonance frequency (~10 kHz) with a high push-pull force when appropriately pre-loaded.
XE scan system
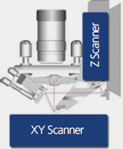
- independent, loop XY and Z flexure scanners for sample and probe tip
XY flexure scanner
- Flat and orthogonal XY scan with low residual bow
XE-Performance
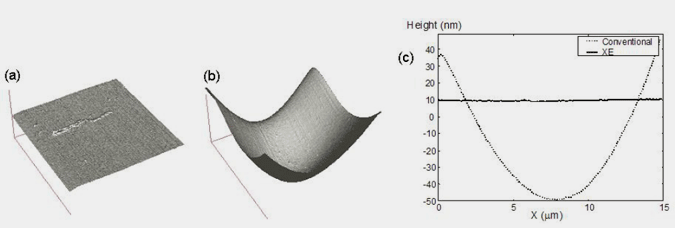 Figure 9. Zero background curvature by Park Systems XE-system (a) and typical background curvature of a conventional AFM system with a tube scanner (b). (c) shows the cross-section of these background curvatures.
Figure 9. Zero background curvature by Park Systems XE-system (a) and typical background curvature of a conventional AFM system with a tube scanner (b). (c) shows the cross-section of these background curvatures.
Figure 9. shows unprocessed AFM images of a bare silicon wafer taken with the XE-system (a), and with a conventional AFM (b). Since the silicon wafer is atomically flat, most of the curvatures in the image are scanner-induced artifacts. Figure 9. (c) shows the cross-section of the images in Figure 9. (a) and (b). Since the tube scanner has intrinsic background curvatures, the maximum out-of-plane motion is as much as 80 nm when the X-axis moves 15 μm. The XE scan system has less than 1nm of out-of-plane motion for the same scan range. Another advantage of the XE scan system is its Z-servo response. Figure 10. is an image of a porous polymer sphere (Styrene Divinyl Benzene), whose diameter is about 5 µm, taken with the XE-system in Non-Contact mode. Since the Z-servo response of the XE-system is very accurate, the probe can precisely follow the steep curvature of the polymer sphere as well as small porous surface structures without crashing or sticking to the surface. Figure 11. shows another example that demonstrates the high performance of the z-servo response with a flat background.

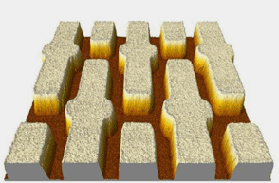
Figure 10. Figure 11.
Better tip life, sample preservation, and accuracy with True Non-Contact™ Mode
In True Non-Contact™ Mode, the tip-sample distance is successfully maintained at a few nanometers in the net attractive regime of inter-atomic force. The small amplitude of tip oscillation minimizes the tip-sample interaction, resulting in superb tip preservation and negligible sample modification.
True Non-Contact™ Mode

- Less tip wear = Prolonged high-resolution scan
- Non-destructive tip-sample interaction = Minimized sample modification
- Immunity from parameter-dependent results
Tapping Imaging
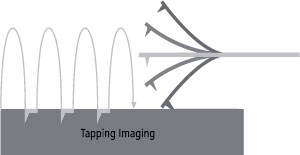
- Quick tip wear = Blurred low-resolution scan
- Destructive tip-sample interaction = Sample damage and modification
- Highly parameter-dependent
Longer Tip Life and Less Sample Damage
The sharp end of an AFM tip is so brittle that once it touches a sample, it becomes instantly blunt and limits the resolution of an AFM, and reduces the quality of the image. For softer samples, the tip will damage the sample and also result in inaccuracies of sample height measurements. Consequently, preserving tip integrity enables consistent high resolution and accurate data. True Non-Contact Mode of the XE-AFM superbly preserves the tip, resulting in much longer tip life and less sample damage the figure, displayed in 1:1 aspect ratio, shows the unprocessed raw data image of a shallow trench isolation sample imaged by the XE-AFM, whose depth is also confirmed by scanning electron microscope (SEM). The same tip used in the imaging of the sample shows no tip wear even after taking 20 images. 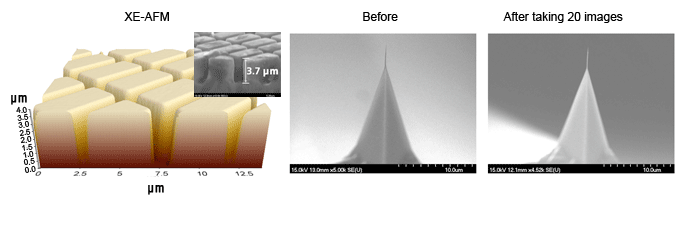
Atomic Force Microscope Surface Analysis & Morphology